Vật liệu nội kiểm (hay control material) đóng vai trò quan trọng trong kiểm soát chất lượng tại phòng xét nghiệm. Nó giúp theo dõi, đánh giá sự chính xác của kết quả xét nghiệm trước khi trả cho bệnh nhân. Qua đó giúp bác sỹ lâm sàng chẩn đoán và điều trị bệnh hiệu quả.
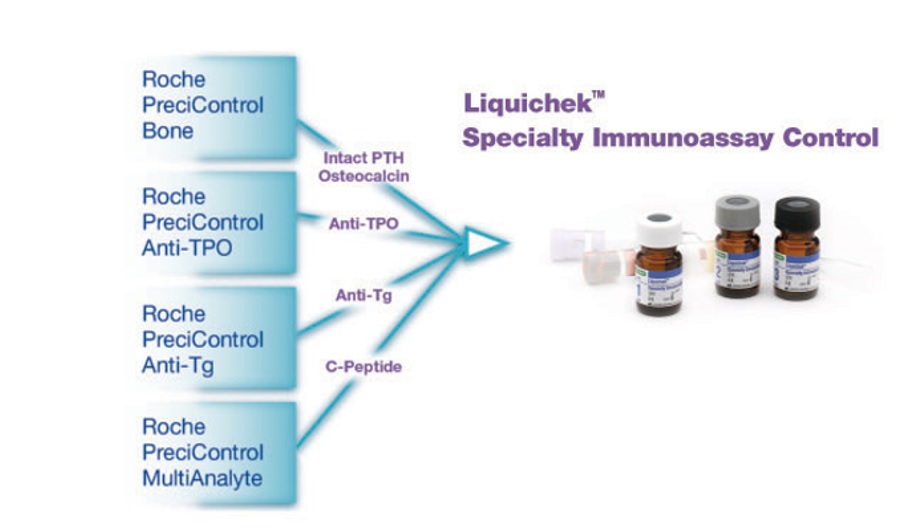
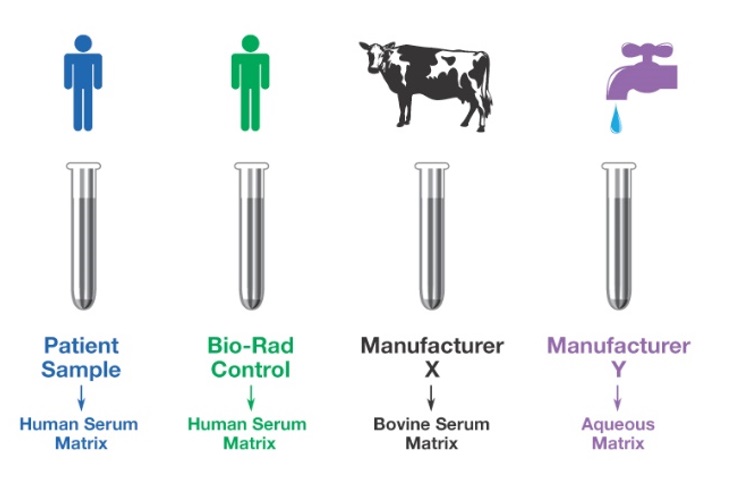
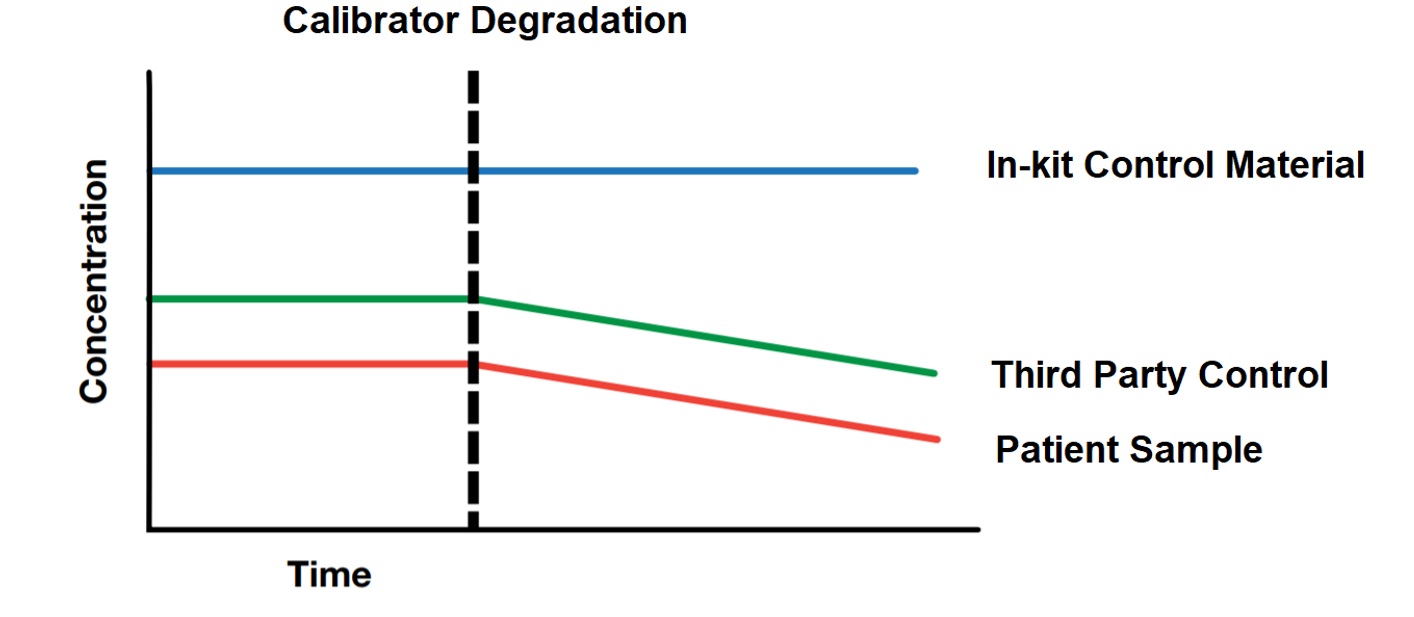
Trong lĩnh vực thiết bị y tế, có nhiều hãng cung cấp một giải pháp tổng thể cho khách hàng, bao gồm cả thiết bị xét nghiệm, hóa chất, vật liệu hiệu chuẩn (Calibrator) và vật liệu nội kiểm. Vật liệu nội kiểm này được sản xuất dành riêng cho hệ thống xét nghiệm của hãng, hay một số hãng sản xuất nội kiểm và Calibrator với cùng một loại vật liệu. Điều này khiến cho nội kiểm theo máy ít nhạy cảm với những thay đổi của thiết bị, hóa chất hay vật liệu Calibrator. Từ đó có thể dẫn đến việc bỏ qua những sai số hệ thống, và chấp nhận trả kết quả không phù hợp với tình trạng lâm sàng của bệnh nhân. Chính vì lý do đó, nhiều tổ chức quốc tế(1) đã khuyến cáo sử dụng nội kiểm độc lập (nội kiểm bên thứ 3), nhằm theo dõi các yếu tố ảnh hưởng đến kết quả bệnh nhân một cách khách quan, hiệu quả hơn. Để hiểu thêm về sự khác biệt giữa nội kiểm theo máy (nội kiểm in-kit) và nội kiểm độc lập, chúng ta có thể theo dõi ở bảng dưới dây:
(1) Khuyến cáo quốc tế
1. ISO 15189:2012
“The laboratory shall use quality control materials that react to the examining system in a manner as close as possible to patient samples”. “Use of independent third party control materials should be considered, either instead of, or in addition to, any control materials supplied by the reagent or instrument manufacturer”
2. CLSI - C24-A3, Statistical Quality Control for Quantitative Measurement Procedures: Principles and Definitions; Approved Guideline—Third Edition, 6.2.1 Relation to Calibrators
“. . . quality control materials should be different from the calibrator materials to ensure that the nội kiểm procedure provides an independent assessment of the measurement procedure’s performance in its entirety, including the procedure for calibration of the measurement.”
3. CLIA - 42 CFR Part 493.1256 Medicare, Medicaid, and CLIA Programs; Laboratory Requirements Relating to Quality Systems and Certain Personnel Qualifications; Final Rule
“For each test system, the laboratory is responsible for having control procedures that monitor the accuracy and precision of the complete analytical process.”
4. NATA (National Association of Testing Authorities) AS 4633 (ISO 15189), Australia, 5.6.1 Internal Quality Control
“Controls independent of those produced by the manufacturer of the test or analyzer should be used.” “The laboratory must have a system of long-term monitoring of internal quality control results to assess method performance.”
5. nội kiểmI - Essential Standards for Registration of Medical Testing Laboratories in India, Quality Council of India 3.5.2 Quality Assurance
“Medical laboratories shall perform internal quality control. Use of third party human matrix quality control is recommended for all analytes.”
6. Laboratory Accreditation Scheme of Malaysia 5.6.1 Quality Control
“The use of controls independent of those produced by the manufacturer of the test or analyzer is preferable”
7. Rili-BÄK - Guideline of the German Medical Association on Quality Assurance in Medical Laboratory Examinations (Rili-BÄK). J Lab Med 2015; 31:26-69. Clause B1, 2.1.1 Procedure (5).
“The control samples must be similar as possible to the patient samples being examined. Within the same measuring procedure the control and the calibration materials must not be identical”





